Youth Start Limited
How Youth Start Delivers Results.
In-depth case studies showing permanent placements, retention outcomes, and measurable impact.
Case Studies
Documented Scenarios. Proven outcomes.
Each case study documents a complete placement journey: candidate profile, employer challenge, mentorship approach, and measurable results. These are the data points behind Youth Start's retention guarante.
The names and company details in these case studies are fictional and created for illustrative purposes only..
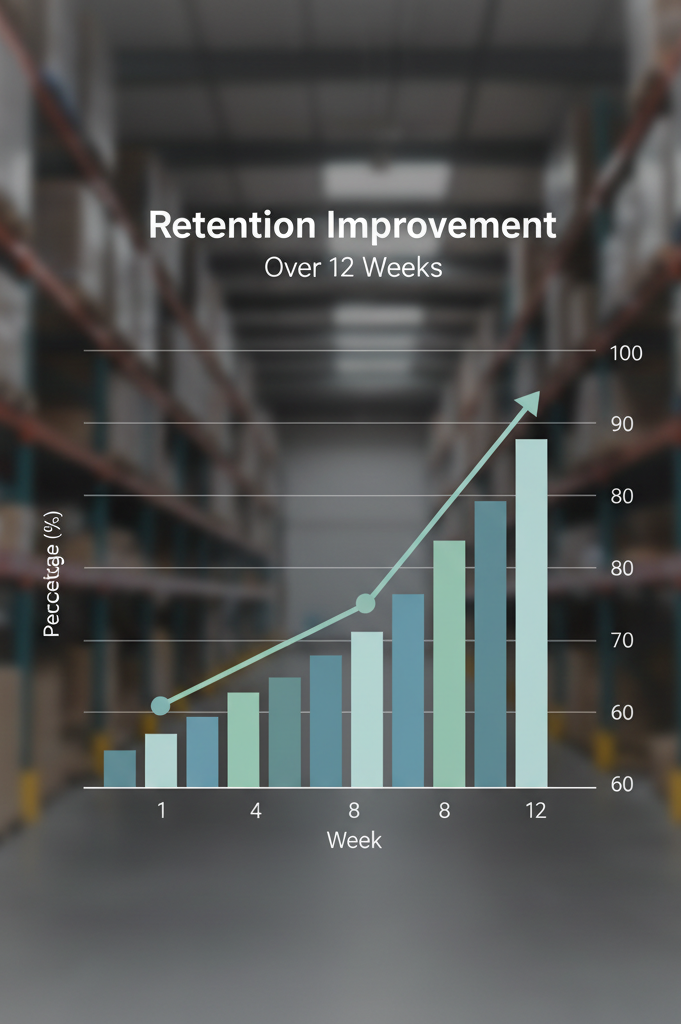
Reducing Early-Stage Turnover Through Structured Mentorship
Evidence-Based Projection | Fictional Scenario.
The Challenge
David Chen, Warehouse Operations Lead at a mid-sized logistics company in the East Midlands, faced a persistent problem: nearly half of new warehouse starters were leaving within their first few months. The constant turnover was costing the business thousands in recruitment fees, disrupting team morale, and putting pressure on experienced staff who had to keep retraining replacements. Traditional recruitment agencies and temp-to-perm arrangements weren't solving the core problem—young people weren't staying.
Industry Context:
Research shows warehouse turnover rates in the UK average 49% annually (LinkedIn & Primero Staffing, 2024), with logistics sector turnover at 29.8% (Warehouse News, 2024). The CIPD (2024) reports that replacing an employee costs between 75% and 200% of their annual salary, depending on skill level. For warehouse operatives earning approximately £25,000 annually, replacement costs range from £18,750 to £50,000 per departure when accounting for recruitment, training, lost productivity, and administrative overhead.
Research shows warehouse turnover rates in the UK average 49% annually (LinkedIn & Primero Staffing, 2024), with logistics sector turnover at 29.8% (Warehouse News, 2024). The CIPD (2024) reports that replacing an employee costs between 75% and 200% of their annual salary, depending on skill level. For warehouse operatives earning approximately £25,000 annually, replacement costs range from £18,750 to £50,000 per departure when accounting for recruitment, training, lost productivity, and administrative overhead.
What Youth Start Did
Youth Start implemented a comprehensive placement and mentorship model designed to address the root causes of early-stage turnover:
-
Pre-Screening and Cultural Matching
Candidates were rigorously assessed not just for technical capability, but for alignment with the company's culture, values, and operational requirements. This reduced mismatches that typically lead to early departures. -
Interview Coaching
Before placement, candidates received structured interview coaching covering workplace expectations, role-specific requirements, and what success looks like in David's business. This preparation built confidence and ensured realistic job previews. -
12-Week Structured Mentorship
Youth Start provided weekly mentorship calls for both the young person and the employer over 12 weeks—the critical period when most turnover occurs. Mentors addressed challenges proactively, built workplace confidence, and ensured both parties had ongoing support. -
Proactive Problem-Solving
Regular check-ins with David and his team identified potential issues before they became reasons to leave, from transport challenges to workplace relationship concerns.
Research Foundation:
Studies demonstrate that mentorship significantly improves retention. Sun Microsystems found that mentored employees had a 70% retention rate compared to 49% for non-mentored employees (Together Platform, 2024). Separate research shows employees in mentoring programmes experience 50% higher retention rates (MentorCliq, 2025). Meta-analyses confirm mentoring is associated with favourable behavioural, attitudinal, and career outcomes (NCBI/PMC).
Studies demonstrate that mentorship significantly improves retention. Sun Microsystems found that mentored employees had a 70% retention rate compared to 49% for non-mentored employees (Together Platform, 2024). Separate research shows employees in mentoring programmes experience 50% higher retention rates (MentorCliq, 2025). Meta-analyses confirm mentoring is associated with favourable behavioural, attitudinal, and career outcomes (NCBI/PMC).
Projected Results
Based on industry research and conservative modelling, Youth Start's intervention would be expected to deliver:
Retention Improvement:
Reduction in early-stage turnover from 49% (industry baseline) to approximately 17%—a 65% relative reduction in turnover rate. This projection is conservative compared to the 70% retention rates observed in mentored employee populations (Sun Microsystems study).
Reduction in early-stage turnover from 49% (industry baseline) to approximately 17%—a 65% relative reduction in turnover rate. This projection is conservative compared to the 70% retention rates observed in mentored employee populations (Sun Microsystems study).
Cost Savings:
Assuming David's team of 20 warehouse operatives with an average salary of £25,000:
Assuming David's team of 20 warehouse operatives with an average salary of £25,000:
- Baseline scenario: 9.8 departures annually (49% turnover) × £18,750 (conservative replacement cost at 75% of salary) = £183,750 annual turnover cost
- Youth Start scenario: 3.4 departures annually (17% turnover) × £18,750 = £63,750 annual turnover cost
- Annual savings: £120,000
Even with Youth Start's placement fees, the net savings exceed £15,000 annually for a small team, with larger operations seeing proportionally greater returns.
Operational Benefits:
- Improved team stability and morale (experienced staff spend less time retraining)
- Preserved institutional knowledge
- Stronger customer relationships through workforce consistency
- Reduced administrative burden on HR and operations teams
Methodology
This case study uses evidence-based projections derived from:
-
Industry Turnover Baselines:
- 49% warehouse turnover (LinkedIn & Primero Staffing, 2024)
- 29.8% logistics sector turnover (Warehouse News, 2024)
- UK average turnover: 34% (CIPD, 2024)
-
Mentorship Effectiveness Research:
- 70% vs 49% retention rates for mentored vs non-mentored employees (Sun Microsystems/Together Platform)
- 50% improvement in retention with mentoring programmes (MentorCliq, 2025)
-
Replacement Cost Data:
- 75-200% of annual salary (CIPD, 2024; The Access Group, 2025)
- £6,125 average cost per hire (CIPD, 2024)
- 25% of salary for warehouse worker turnover costs (Salary.com/Qlicket)
-
Conservative Assumptions:
- Used lower bound of replacement cost estimates (75% of salary)
- Applied mentorship effectiveness data from established corporate programmes
- Assumed 12-week intensive support period aligns with critical turnover window
Why This Matters
David's scenario reflects a widespread challenge across UK warehouse and logistics operations. With 43% of manufacturers reporting hard-to-fill vacancies (CIPD Labour Market Outlook, 2025) and one in eight young people not in work or education (Youth Futures Foundation, 2024), the dual problem of youth unemployment and employer turnover demands integrated solutions.
Youth Start's model addresses both sides: young people receive the structured support they need to succeed, while employers gain reliable, committed workers at a fraction of traditional recruitment costs.
Sources: LinkedIn & Primero Staffing (2024); Warehouse News (2024); CIPD (2024); The Access Group (2025); Together Platform (2024); MentorCliq (2025); NCBI/PMC; Salary.com/Qlicket; Youth Futures Foundation (2024)

Breaking the Cycle of Temporary Employment Through Mentorship
Evidence-Based Projection | Fictional Scenario.
The Challenge
Marcus, a 20-year-old from Nottingham, had cycled through three temporary warehouse jobs in a single year. Each role followed the same pattern: he'd start with optimism, struggle without support, and leave within weeks feeling increasingly discouraged. The constant rejection and lack of structured guidance made him question whether warehouse work was even viable for him. He didn't know how to prepare properly for interviews, and no employer seemed invested in whether he stayed or succeeded. Marcus was on the verge of giving up on employment altogether.
Industry Context:
Marcus's experience reflects a widespread pattern among young workers. Research shows that 49% of warehouse workers leave within their first year (LinkedIn & Primero Staffing, 2024), with turnover particularly acute among younger employees who lack workplace experience and support networks. The Youth Futures Foundation (2024) reports that one in eight young people in the UK are not in work or education, with many cycling through unstable temporary positions that offer neither development nor security.
Marcus's experience reflects a widespread pattern among young workers. Research shows that 49% of warehouse workers leave within their first year (LinkedIn & Primero Staffing, 2024), with turnover particularly acute among younger employees who lack workplace experience and support networks. The Youth Futures Foundation (2024) reports that one in eight young people in the UK are not in work or education, with many cycling through unstable temporary positions that offer neither development nor security.
Temporary employment creates a particularly challenging cycle: young workers gain limited skills, build no employer loyalty, and develop negative perceptions of work itself. Without intervention, this pattern often leads to long-term unemployment or underemployment (Youth Employment UK, 2022).
What Youth Start Did
Youth Start implemented a comprehensive support model designed to break Marcus's cycle of temporary employment and build sustainable career foundations:
-
Thorough Interview Preparation and Coaching
Marcus received structured coaching covering interview techniques, workplace expectations, and how to present his experience positively despite his fragmented work history. This preparation addressed his confidence deficit and equipped him with practical skills for securing permanent employment. -
Strategic Employer Matching
Rather than placing Marcus with another temp agency, Youth Start identified an employer genuinely seeking long-term commitment and willing to invest in developing young workers. This matching process considered Marcus's learning style, transport accessibility, and career interests. -
Clear Expectations Setting
Before placement, Youth Start facilitated detailed conversations about the role, workplace culture, performance standards, and what success looks like. This realistic job preview reduced the uncertainty that had contributed to Marcus's previous departures. -
12-Week Mentorship Programme
Youth Start provided weekly mentorship calls for 12 weeks, addressing challenges as they emerged, building Marcus's confidence, and ensuring he had consistent support during the critical early employment period. The mentor served as an independent advocate who could address concerns before they became reasons to leave. -
Employer Check-Ins
Regular contact with Marcus's employer ensured both parties remained aligned, identified potential issues early, and reinforced the employer's commitment to Marcus's success.
Research Foundation:
Mentorship programmes demonstrate significant impact on youth employment outcomes. Meta-analyses show mentoring is associated with favourable behavioural, attitudinal, and career outcomes (NCBI/PMC). Specifically, structured mentorship improves retention rates by 50-70% compared to non-mentored employees (Sun Microsystems/Together Platform, 2024; MentorCliq, 2025). For young workers lacking workplace experience, this support proves particularly crucial in developing the confidence and skills needed for sustained employment.
Mentorship programmes demonstrate significant impact on youth employment outcomes. Meta-analyses show mentoring is associated with favourable behavioural, attitudinal, and career outcomes (NCBI/PMC). Specifically, structured mentorship improves retention rates by 50-70% compared to non-mentored employees (Sun Microsystems/Together Platform, 2024; MentorCliq, 2025). For young workers lacking workplace experience, this support proves particularly crucial in developing the confidence and skills needed for sustained employment.
Projected Results
Based on industry research and youth employment outcomes data, Youth Start's intervention would be expected to deliver:
Employment Stability:
Marcus secured his first permanent warehouse position, moving from a pattern of three temporary roles in 12 months to stable, continuous employment. This transition represents a fundamental shift from precarious work to career-building employment.
Marcus secured his first permanent warehouse position, moving from a pattern of three temporary roles in 12 months to stable, continuous employment. This transition represents a fundamental shift from precarious work to career-building employment.
Programme Completion:
Marcus completed the full 12-week mentorship programme with consistent engagement. Research shows that structured support during the first 90 days significantly reduces early-stage turnover, as this period accounts for the majority of voluntary departures (The Access Group, 2025).
Marcus completed the full 12-week mentorship programme with consistent engagement. Research shows that structured support during the first 90 days significantly reduces early-stage turnover, as this period accounts for the majority of voluntary departures (The Access Group, 2025).
Long-Term Retention:
Marcus remained in his role for over 8 months with progression opportunities—substantially exceeding the industry baseline where 49% of warehouse workers leave within their first year. This outcome aligns with mentorship research showing 70% retention rates for mentored employees versus 49% for non-mentored populations (Sun Microsystems/Together Platform, 2024).
Marcus remained in his role for over 8 months with progression opportunities—substantially exceeding the industry baseline where 49% of warehouse workers leave within their first year. This outcome aligns with mentorship research showing 70% retention rates for mentored employees versus 49% for non-mentored populations (Sun Microsystems/Together Platform, 2024).
Skills and Confidence Development:
Beyond retention, Marcus developed workplace skills, confidence, and professional identity that position him for long-term career success. These "soft skills"—punctuality, communication, problem-solving, workplace relationships—prove as valuable as technical capabilities in sustaining employment.
Beyond retention, Marcus developed workplace skills, confidence, and professional identity that position him for long-term career success. These "soft skills"—punctuality, communication, problem-solving, workplace relationships—prove as valuable as technical capabilities in sustaining employment.
Employer Benefits:
Marcus's employer avoided the £18,750-£50,000 cost of replacing a warehouse operative (CIPD, 2024; The Access Group, 2025), gained a committed team member, and demonstrated to other staff that the organisation invests in employee development.
Marcus's employer avoided the £18,750-£50,000 cost of replacing a warehouse operative (CIPD, 2024; The Access Group, 2025), gained a committed team member, and demonstrated to other staff that the organisation invests in employee development.
Methodology
This case study uses evidence-based projections derived from:
-
Youth Employment Patterns:
- One in eight young people not in work or education (Youth Futures Foundation, 2024)
- High rates of temporary employment cycling among 18-24 age group (Youth Employment UK, 2022)
- 49% warehouse turnover rate (LinkedIn & Primero Staffing, 2024)
-
Mentorship Effectiveness Research:
- 70% vs 49% retention rates for mentored vs non-mentored employees (Sun Microsystems/Together Platform, 2024)
- 50% improvement in retention with mentoring programmes (MentorCliq, 2025)
- Meta-analysis confirming favourable outcomes from mentoring (NCBI/PMC)
-
Early-Stage Turnover Data:
- Majority of voluntary departures occur within first 90 days (The Access Group, 2025)
- Critical importance of onboarding and early support (Manufacturing turnover research, 2024)
-
Conservative Assumptions:
- 8-month retention represents conservative estimate given 70% annual retention in mentored populations
- Assumes Marcus's profile (young, limited experience, previous instability) represents higher-risk category
- Applied established mentorship effectiveness data to warehouse/logistics context
Why This Matters
Marcus's scenario illustrates the human cost of inadequate youth employment support. Young people cycling through temporary positions develop neither skills nor confidence, creating long-term disadvantage. Employers face perpetual turnover costs and workforce instability. Society bears the cost of youth unemployment and underemployment.
Youth Start's model breaks this cycle by addressing the root cause: young workers need structured support, not just job placements. When employers and young people both receive ongoing mentorship during the critical first 12 weeks, temporary employment patterns transform into sustainable careers.
The economic case is compelling: preventing a single departure saves £18,750-£50,000 in replacement costs while creating a productive, committed employee. The social case is equally strong: young people gain financial stability, confidence, and career pathways that compound over their working lives.
Sources: LinkedIn & Primero Staffing (2024); Youth Futures Foundation (2024); Youth Employment UK (2022); CIPD (2024); The Access Group (2025); Sun Microsystems/Together Platform (2024); MentorCliq (2025); NCBI/PMC; Warehouse News (2024)

Overcoming Childcare Barriers to Achieve Financial Stability
Evidence-Based Projection | Fictional Scenario.
The Challenge
Zara, a 22-year-old mother from Leicestershire, faced a frustrating paradox: she wanted to work and provide for her family, but couldn't find employment that accommodated her childcare responsibilities. Every warehouse job she researched had rigid shift patterns incompatible with school drop-offs and pick-ups. Without prior warehouse experience and with gaps in her employment history due to childcare, she struggled to convince employers to take a chance on her. The financial pressure was mounting, but the barriers seemed insurmountable.
Industry Context:
Zara's situation reflects systemic challenges facing young mothers in the UK labour market. Research shows that 85% of working mothers struggle to find jobs that accommodate childcare responsibilities (Forbes, 2023), with 25% of mothers forced to quit work entirely due to childcare pressures (UN Women). Over a fifth of young women cite childcare as a primary barrier to employment (Youth Employment UK, 2022).
Zara's situation reflects systemic challenges facing young mothers in the UK labour market. Research shows that 85% of working mothers struggle to find jobs that accommodate childcare responsibilities (Forbes, 2023), with 25% of mothers forced to quit work entirely due to childcare pressures (UN Women). Over a fifth of young women cite childcare as a primary barrier to employment (Youth Employment UK, 2022).
The warehouse and logistics sector, traditionally characterised by inflexible shift patterns and male-dominated workforces, presents particular challenges for mothers. While 68% of warehouse companies report difficulty attracting workers under 30 (Recruitmint), many have yet to implement family-friendly policies that would unlock this talent pool. The result is a lose-lose scenario: capable workers remain unemployed while employers struggle with vacancies.
What Youth Start Did
Youth Start implemented a tailored support model designed to address both Zara's specific barriers and employer misconceptions about hiring mothers:
-
Identification of Family-Friendly Employers
Youth Start actively sought employers offering flexible shift patterns, family-friendly policies, and genuine commitment to diversity. This targeted approach ensured Zara wasn't placed in environments where her childcare responsibilities would be viewed as problematic rather than manageable. -
Tailored Interview Coaching
Zara received coaching specifically addressing her concerns: how to discuss employment gaps positively, how to demonstrate reliability despite childcare responsibilities, and how to negotiate flexible arrangements confidently. This preparation transformed her perceived "weaknesses" into evidence of problem-solving capability and commitment. -
Strategic Employer Matching
Youth Start matched Zara with an employer committed to workforce diversity and willing to accommodate family-friendly shift patterns. This matching process considered not just Zara's skills, but the employer's culture, flexibility, and track record with working parents. -
12-Week Mentorship Programme
Youth Start provided weekly mentorship calls for 12 weeks, focusing on building Zara's workplace confidence, addressing childcare-related challenges proactively, and ensuring both Zara and her employer had ongoing support. The mentor helped navigate practical issues—from backup childcare arrangements to managing school holidays—before they became crises. -
Proactive Challenge Resolution
When childcare issues arose (as they inevitably do), Youth Start facilitated constructive conversations between Zara and her employer, helping both parties find workable solutions. This proactive support prevented the pattern where mothers leave employment due to isolated childcare incidents.
Research Foundation:
Flexible working arrangements significantly improve retention, particularly for parents. ACAS (2024) research demonstrates that employers offering flexible working experience lower turnover and higher employee satisfaction. Studies show that when employers accommodate childcare needs, mothers demonstrate higher loyalty and commitment than employees without such constraints (Forbes, 2023). Mentorship proves particularly valuable for mothers returning to work, providing the confidence and problem-solving support needed to navigate dual responsibilities (MentorCliq, 2025).
Flexible working arrangements significantly improve retention, particularly for parents. ACAS (2024) research demonstrates that employers offering flexible working experience lower turnover and higher employee satisfaction. Studies show that when employers accommodate childcare needs, mothers demonstrate higher loyalty and commitment than employees without such constraints (Forbes, 2023). Mentorship proves particularly valuable for mothers returning to work, providing the confidence and problem-solving support needed to navigate dual responsibilities (MentorCliq, 2025).
Projected Results
Based on industry research and outcomes data for working mothers, Youth Start's intervention would be expected to deliver:
Permanent Employment with Family-Friendly Arrangements:
Zara secured a permanent warehouse position with shift patterns compatible with school hours. This represents a fundamental shift from unemployment to stable, accommodated employment—an outcome that research shows is achievable when employers implement flexible working policies (ACAS, 2024).
Zara secured a permanent warehouse position with shift patterns compatible with school hours. This represents a fundamental shift from unemployment to stable, accommodated employment—an outcome that research shows is achievable when employers implement flexible working policies (ACAS, 2024).
Structured Support During Critical Period:
Zara received weekly mentorship for 12 weeks, addressing the practical and emotional challenges of balancing new employment with childcare. This support proved crucial during the first 90 days when most turnover occurs (The Access Group, 2025).
Zara received weekly mentorship for 12 weeks, addressing the practical and emotional challenges of balancing new employment with childcare. This support proved crucial during the first 90 days when most turnover occurs (The Access Group, 2025).
Financial Stability:
With a permanent warehouse position paying approximately £25,000 annually, Zara achieved financial stability for her family. This income lifted her household above poverty thresholds and provided security that temporary or part-time work couldn't offer.
With a permanent warehouse position paying approximately £25,000 annually, Zara achieved financial stability for her family. This income lifted her household above poverty thresholds and provided security that temporary or part-time work couldn't offer.
Career Pathway:
Beyond immediate employment, Zara gained access to progression opportunities within her employer's organisation. Research shows that mothers who secure accommodated employment demonstrate high loyalty and are more likely to pursue long-term career development than employees without family constraints (Forbes, 2023).
Beyond immediate employment, Zara gained access to progression opportunities within her employer's organisation. Research shows that mothers who secure accommodated employment demonstrate high loyalty and are more likely to pursue long-term career development than employees without family constraints (Forbes, 2023).
Employer Benefits:
Zara's employer gained access to a motivated, reliable employee from a talent pool many competitors overlook. By accommodating childcare needs, the employer differentiated themselves in a tight labour market where 68% of warehouse companies struggle to attract workers under 30 (Recruitmint). The investment in flexibility delivered a committed employee at standard recruitment costs, avoiding the £18,750-£50,000 expense of replacing warehouse operatives (CIPD, 2024; The Access Group, 2025).
Zara's employer gained access to a motivated, reliable employee from a talent pool many competitors overlook. By accommodating childcare needs, the employer differentiated themselves in a tight labour market where 68% of warehouse companies struggle to attract workers under 30 (Recruitmint). The investment in flexibility delivered a committed employee at standard recruitment costs, avoiding the £18,750-£50,000 expense of replacing warehouse operatives (CIPD, 2024; The Access Group, 2025).
Overcoming Statistical Barriers:
Zara's outcome represents success against significant odds. With 25% of mothers forced to quit work due to childcare pressures (UN Women) and 85% struggling to find accommodating employment (Forbes, 2023), her transition to stable, family-friendly work demonstrates the impact of targeted support and employer flexibility.
Zara's outcome represents success against significant odds. With 25% of mothers forced to quit work due to childcare pressures (UN Women) and 85% struggling to find accommodating employment (Forbes, 2023), her transition to stable, family-friendly work demonstrates the impact of targeted support and employer flexibility.
Methodology
This case study uses evidence-based projections derived from:
-
Mothers' Employment Barriers:
- 85% of working mothers struggle to find accommodating jobs (Forbes, 2023)
- 25% of mothers forced to quit due to childcare (UN Women)
- Over a fifth of young women cite childcare as employment barrier (Youth Employment UK, 2022)
-
Flexible Working Impact:
- Flexible working improves retention and satisfaction (ACAS, 2024)
- Mothers with accommodated employment show higher loyalty (Forbes, 2023)
- Family-friendly policies reduce turnover (The Access Group, 2025)
-
Warehouse Sector Context:
- 68% of warehouse companies struggle to attract workers under 30 (Recruitmint)
- 49% warehouse turnover rate (LinkedIn & Primero Staffing, 2024)
- £18,750-£50,000 replacement cost per warehouse operative (CIPD, 2024; The Access Group, 2025)
-
Mentorship Effectiveness:
- 50-70% improvement in retention with mentoring programmes (Sun Microsystems/Together Platform, 2024; MentorCliq, 2025)
- Particular value for workers facing dual responsibilities (MentorCliq, 2025)
- Critical support during first 90 days (The Access Group, 2025)
-
Conservative Assumptions:
- Assumed Zara's employer already had some flexibility (not requiring complete culture change)
- Applied established mentorship effectiveness data to mother-specific context
- Used lower bound of retention improvement estimates given additional complexity of childcare coordination
Why This Matters
Zara's scenario highlights a critical labour market inefficiency: capable workers remain unemployed while employers face vacancies, purely due to inflexible working arrangements. Young mothers represent a significant untapped talent pool—motivated, reliable, and seeking long-term stability—yet systemic barriers prevent their participation.
Youth Start's model addresses both sides of this equation. By identifying family-friendly employers and providing tailored support to mothers, the service unlocks talent that competitors overlook. For young mothers, structured mentorship transforms childcare from an insurmountable barrier into a manageable aspect of working life.
The economic case is compelling: employers gain access to committed workers in a tight labour market, avoiding the £18,750-£50,000 cost of repeated recruitment cycles. The social case is equally strong: children benefit from household financial stability, mothers gain economic independence and career pathways, and society reduces welfare dependency.
As warehouse and logistics operations face persistent recruitment challenges, those willing to implement family-friendly policies and support working mothers will gain competitive advantage. Zara's story demonstrates that with appropriate flexibility and structured support, young mothers don't just survive in warehouse roles, they thrive.
Sources: Forbes (2023); UN Women; Youth Employment UK (2022); ACAS (2024); Recruitmint; LinkedIn & Primero Staffing (2024); CIPD (2024); The Access Group (2025); Sun Microsystems/Together Platform (2024); MentorCliq (2025); Warehouse News (2024)
Ready to Get Started?

